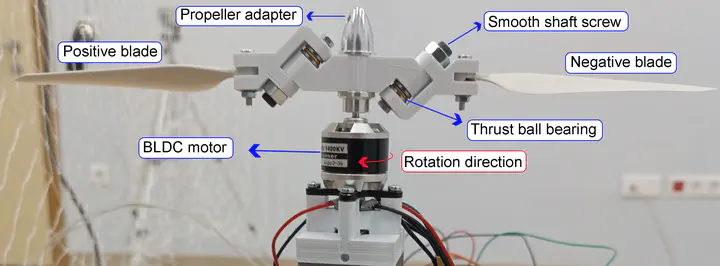
Abstract
Micro Aerial Robots (MARs) are expected to increase their payload carrying capacity and flight time, and to serve in limited areas. These demands can only be met by developing new designs such as the swashplateless mechanism. By using the developed swashplateless mechanisms in aerial robots, the number of actuators and power consumption are reduced and payload carrying capacities are increased. Design criteria of swashplateless mechanisms should be determined according to the working conditions of aerial robots. In this paper, different hinge angles are characterized for aerial robots that will use the swashplateless passive mechanism. This characterization is investigated with respect to design criteria such as power consumption, thrust force and RPM and sound pressure level (SPL) of the swashplateless mechanism with different hinge angles. According to the results obtained, it was revealed that changes occurred in the thrust force characterizations of the mechanisms with different hinge angles before and after 1750 RPM. Similarly, it has been shown that a change in the power consumption behavior of passive mechanisms with different hinge angles occurs before and after the 0.8 N thrust force threshold value. The effect of determining the hinge angle in the swashplateless mechanism on the system performance is revealed. It has been shown that if the swashplateless mechanism is to be used in the aerial robot, it is necessary to first determine the working conditions during operational use and then determine the hinge angle in the passive mechanism.